In modern transportation, the electrified third rail system stands as a testament to efficiency and sustainability, providing indispensable power to trains. The operation of this innovative technology, however, comes with a crucial responsibility—the safety of electrified tracks. Managing high-voltage electrification and preventing accidents demands a careful approach, and the proper functioning of specialized third rail train equipment is integral to this pursuit. Hence, this article explains the significance of third rail safety and the measures transit authorities and industries must adopt to navigate the challenges effectively, ensuring the well-being of passengers and workers alike.
The Third Rail System – Efficient and Sustainable Power
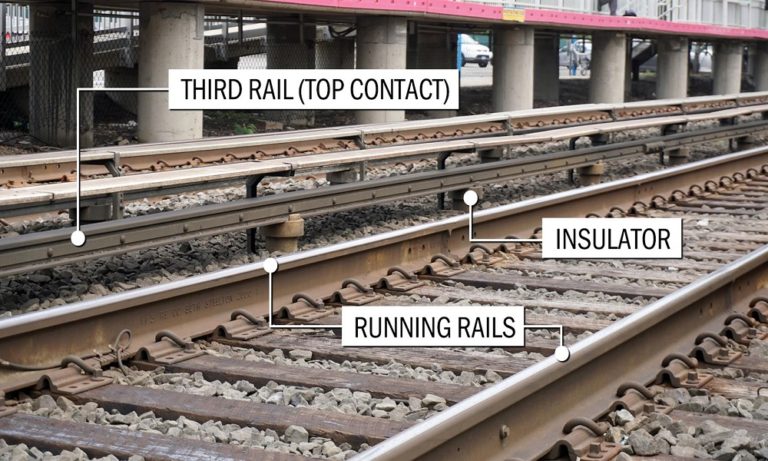
The third rail system has become a cornerstone of modern transit, providing electricity to trains through a separate rail positioned beside the tracks. This electrification method eliminates the need for diesel engines, resulting in quieter and more eco-friendly train operations. However, the electrified nature of the third rail system requires careful safety considerations to prevent accidents and potential hazards.
Challenges of High-Voltage Electrification
The primary challenge of the third rail system lies in managing the high-voltage electric current that powers the trains. Accidental contact with the electrified rail can lead to severe consequences, posing risks to both passengers and rail personnel. As such, transit authorities and industries must implement robust safety measures to minimize the possibility of such incidents.
Critical Role of Third Rail Train Equipment
Specialized third rail train equipment, such as collector shoes and pantographs, plays a crucial role in the safe operation of electrified tracks. These equipment pieces facilitate controlled contact with the electrified rail, allowing trains to draw power while maintaining safety standards. Proper maintenance and upkeep of these equipment pieces are essential to ensure the reliable functioning of the third rail system.
Isolation and Enclosure – Safeguarding against Accidents
To mitigate the risk of accidental contact with the electrified rail, transit authorities, and industries adopt isolation and enclosure measures. Positioning the third rail within a protective housing or covering it with insulating materials restricts access to specialized train equipment. Additionally, warning signs and fencing are strategically placed along the tracks to deter unauthorized access to the electrified area.
Rigorous Maintenance and Inspections – Ensuring Safety and Reliability
Regular maintenance and inspections are indispensable to ensure the safety and reliability of the third rail system. Strict maintenance schedules allow for the early detection of wear, damage, or electrical issues, enabling timely repairs and replacements. Routine inspections play a vital role in identifying potential hazards and maintaining the integrity of the electrified tracks.
Training and Awareness – Empowering Employees and the Public
A culture of safety is fundamental to the effective operation of the third rail system. Comprehensive training for rail operators and personnel equips them with the knowledge to understand the risks associated with electrified tracks and respond effectively to emergencies. Transit authorities and industries also prioritize raising public awareness through informational campaigns and signage, promoting vigilance and caution around electrified areas.
Conclusion
The third rail system represents a remarkable advancement in modern transit, providing efficient and sustainable power to trains. To ensure the safety of passengers and rail personnel, transit authorities and industries must navigate the challenges of high-voltage electrification with diligence and precision. By investing in specialized third rail train equipment, implementing isolation and enclosure measures, conducting rigorous maintenance and inspections, and promoting training and awareness, the reliability and safety of electrified tracks can be collectively safeguarded. By upholding the highest standards of third rail safety, one can continue to deliver a secure and efficient transit experience for all.